Patch Management
Architecture. Compliance. Deployment Governance.
The Patch Management module executes centralized deployment of OS and third-party updates across distributed environments. This logic eliminates manual update cycles by aligning security remediation with defined maintenance windows. The framework maintains version consistency to mitigate vulnerability exposure without interrupting production workflows.


Integrated Patch Governance and
Remediation Logic
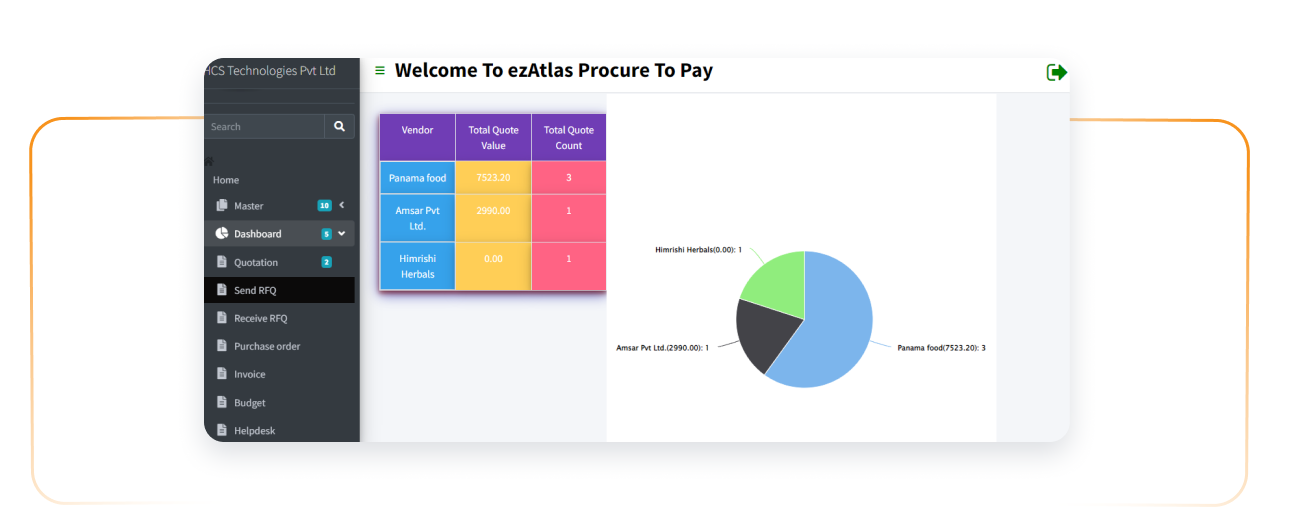

OS & Application Patch Discovery
Scanning agents probe endpoint registries to catalogue missing security updates across diverse OS versions and third-party stacks. Local versioning data is cross-referenced against vulnerability databases to pinpoint specific exposure risks within the infrastructure. This discovery cycle runs via recurring cron-like triggers to maintain an updated gap analysis. Logged findings populate the remediation queue to drive subsequent patching cycles.
Patch Approval Workflows
Administrators enforce multi-stage validation gates to vet updates before production-wide release. This sequence facilitates isolated testing on canary groups to verify package stability and application interoperability. Logic-based routing restricts authorized distribution to verified packages only. Critical threats bypass standard delays through an accelerated fast-track hierarchy when urgent mitigation is required.
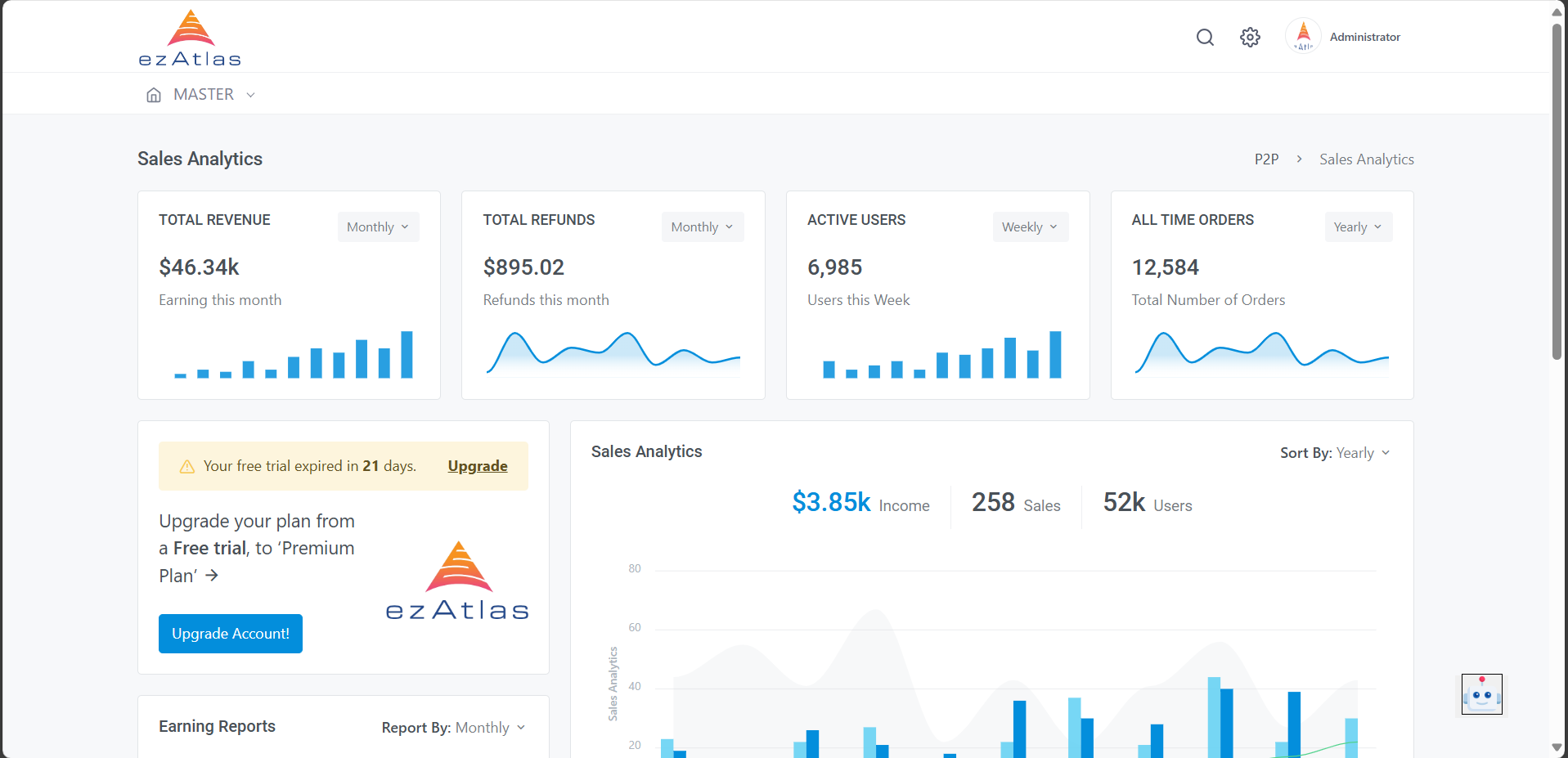
Scheduled & Automated Patch Deployment
The execution engine pushes updates during specified maintenance windows to avoid production-side latency or downtime. Targeting parameters allow for staggered rollouts across departments, time zones, or specific device tiers. Automated distribution utilizes localized caching mechanisms to prevent bandwidth saturation during mass updates. Post-install logic verifies successful deployment and manages necessary system-level reboots.
Compliance Reporting (Patched vs. Non-Patched)
Reporting modules generate a delta analysis between the current fleet status and defined security baselines. Heatmaps and tabular data isolate non-compliant assets resulting from failed installs or persistent offline states. This real-time visibility identifies security voids across the global hardware estate. Data is archived into a historical ledger to document the infrastructure’s security trajectory over time.


Rollback & Failure Handling
Pre-patch snapshots archive system states—immediate reversal triggers if deployment errors occur. Error-trapping mechanisms flag failed installation codes and kill sequences to block stability loss. Recovery protocols revert targeted endpoints to known-good configurations via console. Logs pinpoint failure nodes: specifically package corruption or local hardware conflicts.
Risk-Based Patch Prioritization
Engine logic sorts updates by CVSS scores, forcing high-threat vulnerabilities to queue priority. Filtering isolates zero-day exploits or mission-critical service patches for accelerated deployment. Ranking aligns remediation with risk tolerance instead of chronological order. Impact-weighting shifts resource-heavy updates to specific low-utilization windows.


Integration with Asset Inventory
Patching workflows pull hardware and software data from ITAM repositories to verify compatibility. This sync prevents update attempts on legacy hardware or incompatible OS versions. Asset tags and location data drive granular targeting by department or hardware tier. Records sync discovered assets into global patching schedules.
Audit-Ready Patch Compliance Reports
System-generated ledgers document update states, maintaining tamper-evident records of security hygiene. Reports include timestamps, machine IDs, and KB numbers for regulatory or insurance audits. Automated distribution sends compliance snapshots to stakeholders on recurring schedules. Historical archiving maintains longitudinal views of infrastructure health for security trend analysis.


On-Prem & Distributed Environment Support
Architecture facilitates patch delivery across local data centers and geographically dispersed remote endpoints. Secure tunneling protocols bridge the gap between corporate networks and home-office hardware without VPN reliance. Distribution logic utilizes localized relay points to manage updates for low-bandwidth or intermittent connections. This hybrid-ready framework maintains uniform security standards regardless of physical asset location.
Experience the future of spend management at no initial cost.

